Silica dust
What it is, who is at risk and how to protect workers
Anyone working at a construction site or quarry will be exposed to dust from wood or stone. They can breathe in this dust, known as silica. Find out why this is harmful, along with advice on how to manage exposure.
Facts about silica dust
Individual silica dust particles are so small that they are invisible to the naked eye in normal light. This results in relatively high airborne concentrations with no visible or physical awareness that people are inhaling the dust.
A joint World Health Organization and International Labour Organization report estimates:
- 42,258 global deaths in 2016 attributed to occupational exposure to silica
- 1.3 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) attributed to occupational exposure to silica in the same period.
What is silica?
Silica is a natural substance found in stone, rocks, sand and clay in its crystalline form. It is also found in bricks, tiles, concrete and some plastics. When these materials are worked on, for example when being cut or drilled into, crystalline silica is released as a very fine dust that can be breathed in. This dust causes significant ill-health effects, including silicosis and cancers.
There are other forms of silica that do not have a crystal structure and are referred to as amorphous silica. This can be found in diatomaceous earth, silica gel and synthetic amorphous silica.
Why is silica harmful?
Silica dust is only harmful when it’s inhaled deep into the lungs, where oxygen is transitioned into the blood. Silica can be found in sand but sitting on a sandy beach will not cause any respiratory harm because any sand particles breathed in will generally be too big to go beyond the nose or upper airways. It is the very fine airborne silica dust that can be harmful. This is known as the respirable fraction.
Respirable particles are typically less than around 5 micrometres (μm) in size. Compare this size to the ‘full stop/period’ at the end of the sentence, which is around 200-300 μm in diameter, and the finest sand on the beach, which is about 50-70 μm.
In 1996, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) reviewed the scientific evidence and concluded that crystalline silica dust is carcinogenic to humans. It is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning it is a definite cause of cancer in humans.
Exactly how silica dust causes lung cancer is unclear. The IARC suggests the most likely cause is when silica dust deposits in the lungs, the toxicity makes it difficult for the body’s natural defence cells to remove it. The dust remains in the lungs, causing persistent inflammation. This inflammation can damage deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the lung cells and lead, in some people, to lung cancer.
What is the issue?
When respirable crystalline silica (RCS) is breathed in, it can cause a condition known as silicosis. This can be disabling or even fatal.
Silica dust enters the lungs and causes fibrosis (hardening or scarring) of lung tissue, as the body’s immune system tries to remove the RCS particles. This affects lung function and makes it difficult for the lungs to take in oxygen. People with silicosis will likely experience:
- severe shortness of breath
- coughing
- difficulty in walking short distances, completing tasks or doing exercise
- fatigue and a loss of mobility
- fever
- weight loss
- becoming house- or bed-bound
- chest pain
- premature death, in some cases due to heart failure.
Silicosis usually occurs after 10 to 20 years of occupational exposure to RCS and is diagnosed via chest x-ray. There are three types of silicosis.
- Acute silicosis – occurs after a heavy exposure (over a short-term) to RCS. It can also increase the risk of lung infections such as tuberculosis.
- Accelerated silicosis – occurs after several years of high exposure levels to RCS.
- Chronic silicosis – occurs after more than 10 years of exposure where the scarring and inflammation of the lungs develops over a longer time. This can lead to heart failure and premature death.
Unfortunately, silicosis continues to develop after exposure has ended and there is no cure for the condition. However, silicosis is preventable by controlling exposure to RCS.
Other diseases caused by silica
Lung cancer
Exposure to RCS increases the risk of developing lung cancer and workers with silicosis are at an increased risk of developing the condition.
With lung cancer, abnormal cells grow into tumours that interfere with lung function. The cancer cells can also migrate to other parts of the body and cause further damage.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
This is a collection of long-term lung conditions that can be extremely disabling and even lead to death. Conditions include chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
The lungs and breathing tubes become damaged, making it difficult to breathe. COPD develops slowly and many do not realise they have the disease. It is not usually reversible.
Kidney disease
Workers exposed to RCS are also at an increased risk of developing kidney disease. Kidney failure can occur in those who have had high silica exposures or have silicosis.
Which industries are affected by silica exposure?
Exposure to silica dust occurs in many industries, but particularly in construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and oil and gas. Industries include:
- abrasive blasting
- brick, concrete or tile manufacturing
- bricklaying
- cement finishing
- ceramics manufacturing
- coke and other fuel manufacturing
- construction
- demolition
- foundries
- glass manufacturing
- metals and machinery manufacturing
- mineral product manufacturing
- mining and quarrying
- steel manufacturing
- stonemasonry
- tunnelling.
In fact, anywhere that silica-containing material is cut, ground or drilled.
High-risk activity
Common tasks where people may be exposed include:
- breaking, crushing, grinding or milling silica-containing material such as concrete, aggregate or mortar
- drilling, cutting, chiselling or sanding silica-containing material
- dealing with cement
- moving earth, for example excavating, mining, quarrying or tunnelling
- abrasive blasting or sandblasting
- laying, maintaining or replacing ballast
- handling, mixing or shovelling dry materials that include silica
- using silica, sand or silica-containing products in the manufacturing process of glass and other non-metallic mineral products
- using sand as a moulding medium in foundries
- using silica flour, a finely ground form of crystalline silica
- dry sweeping of materials after a task where silica dust has been created.
It’s not just specific activities, such as drilling or cutting materials that contain RCS, which can expose people to silica dust. As well as disturbing fine silica dust, exposure can occur when someone cleans up after a task. The dust can also:
- stay in the air for a period after work has finished
- be released from clothes or surfaces
- become airborne again when disturbed by people, vehicles or equipment
- be released by equipment leaks or spillages.
How to manage silica dust
Preventing exposure to RCS is the only reliable method to protect workers’ health.
Many countries have set legal exposure limits for silica. These are the maximum allowable concentrations in workplace air, averaged over a period of time (usually eight hours). Check out the table from Industrial Safety and Hygiene News in the related links section on this page.
Measuring silica
A way of assessing the amount of airborne dust is to use a dust lamp, sometimes called a Tyndall beam. It illuminates very fine dust that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye.
A bright beam of light is shone through an area where a particle dust cloud may be present. A flat panel is used to shield the observer’s eyes from the main beam. For example, this could be a piece of card, or by using the worker’s body or a piece of machinery as a shield.
The particle dust cloud is observed behind the shield by looking up the beam towards the source of illumination. The beam should be observed at a slight angle (5-15 degrees) off the centre of the beam. A dark background should be used to help with the observation.
The dust cloud will then be made visible as the particles are suspended in the air. Normal lighting conditions can be used, but better results are obtained by suppressing the ambient lighting. It may be surprising just how much particle dust occupies the air.
Read the Health and Safety Executive’s simple checks to control dust and mist.
The quantitative measurement of exposure to silica requires occupational hygiene support.
An occupational hygienist uses equipment, including a battery-operated sampling pump, polythene tubing, cyclone sampling head, pre-weighed PVC filters, a flowmeter (to measure the amount of air flowing through the sampler), clips and belts.
The equipment is worn by a worker throughout a shift, with the sampling head close to the worker’s nose and mouth area. After the shift, the filter is sent to a specialist laboratory for analysis for crystalline silica.
The result is expressed as a concentration – milligrams of crystalline silica per cubic metre of air sampled (mg/m3). You can also ask the laboratory to reweigh the filter to give the respirable dust concentration and the percentage of silica on the sample.
The data can then be compared with your country’s legal exposure limit.
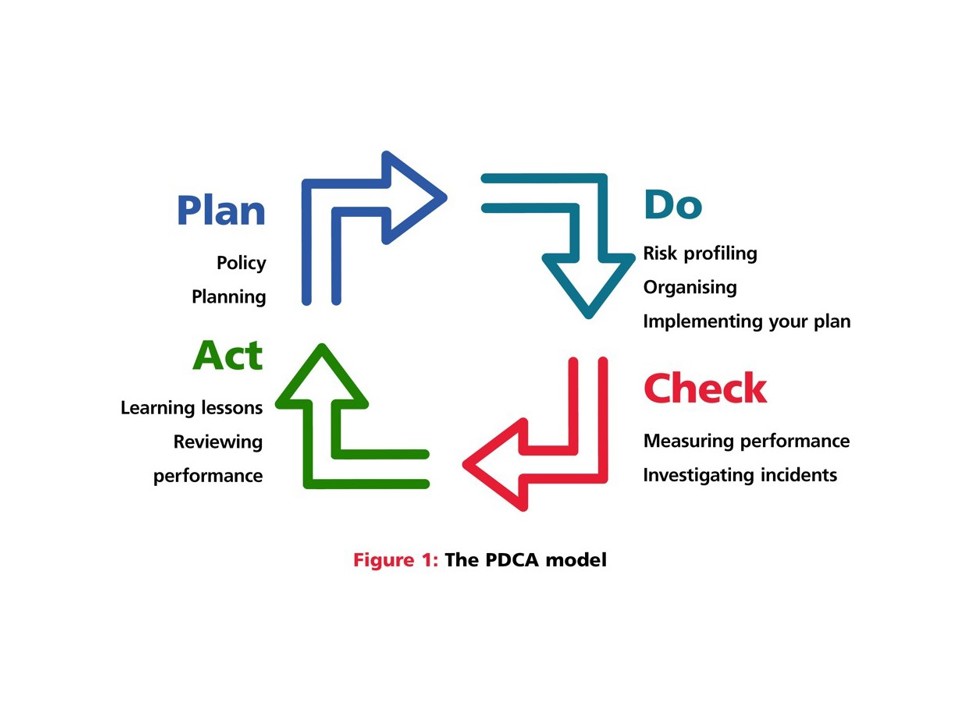
Managers and business owners
Managers and business owners can follow the plan, do, check, act (PDCA) health and safety management system method. There are eight simple steps to avoid worker exposure to RSC.
- identification of workplace tasks that may or do involve RCS exposure
- a risk assessment and description of suitable controls, concentrating where possible on eliminating the risk or extraction systems rather than personal protective equipment (PPE) and respiratory protective equipment (RPE)
- provide robust procedures, also known as safe systems of work, to eliminate or reduce exposure to RCS and restrict access to high-risk RCS work areas
- a plan to review associated risk assessments, procedures and the silica exposure plan itself
- informing workers on what they need to do to manage the risks from working with RCS
- an inspection schedule to ensure the organisation has frequent inspections.
- eliminating RCS from a task by using alternative products where possible
- reducing RCS dusts by using materials with lower silica content where possible
- implementing engineering and administrative controls to reduce RCS exposure
- providing suitable PPE and RPE, where required, to protect workers.
- if the silica exposure plan was accurate and shared
- if local procedures were implemented and followed correctly
- whether those exposed had been informed of the presence of silica
- whether those exposed had been provided with relevant training.
- work history to determine any potential exposures
- health history to identify any health concerns or symptoms
- a physical examination of the respiratory system, which may include an x-ray and a pulmonary function test if required
- testing for latent tuberculosis infection and any other respiratory concerns, as these may increase a worker’s potential to be adversely affected by RCS.
Plan
Appoint a competent person to lead the silica exposure plan
The responsible person should be competent to undertake the task at hand. The exposure plan should cover the following:
Do
Assess organisational silica exposure risks
Consider who might be exposed to silica throughout the organisation. What tasks will they be doing that may exposure them to RCS?
Share silica exposure risks with workers and contractors
As good practice, whether it is law or not in your country, workers who may be exposed to RCS should be informed of the level of risk to health and what precautions they must implement to keep themselves and others safe.
Contractors are much more likely to expose RCS if they are unfamiliar with the location, tasks and materials, so consider how you will make the latest version of the silica exposure plan available to them.
If workers are going to work in or on someone else’s premises, ensure that you find out and they are informed about any potential RCS exposures they may come across in their tasks.
Introduce controls to reduce silica exposure
These will include:
Provide silica information, instructions and training
It is good practice to provide silica awareness training to workers whose working activity may involve exposure to RCS. This education should include where RCS can be found, how to work safely, and how to protect themselves and others from RCS exposure. It is also good practice to demand that any workers or contractors have also received silica awareness training, if their activities potentially involve exposure to RCS. Workers and contractors must be empowered to stop work if they believe they have encountered RCS exposures.
Workers should also be provided with robust procedures when working with RCS, which will reinforce any information and training.
Check
Investigate incidents involving silica exposure
Silica exposure incidents must be investigated to identify causes. The investigation must check:
A note should be made in the personal records of those exposed. Records should include when the incident happened, how long it lasted, and possible exposure levels.
Exposed workers should be submitted to an organisation health monitoring and surveillance programme.
Monitor controls and carry out health surveillance
Monitoring RCS levels is crucial to help prevent exposures. Technological advancements mean that measuring RCS dust is an easier task to complete.
It is important to monitor controls to check whether they are suitable and working to eliminate or reduce RCS exposure.
Health monitoring also has a part to play. Workers should undergo regular health checks by a competent medical professional, this may be through occupational health. These checks will likely include:
Act
Evaluate and apply learning lessons
After any incident and investigation, learning lessons must be recognised and applied to the silica exposure plan and health and safety management system. This helps prevent and reduce the chance of exposures recurring.
Review the silica exposure plan regularly to keep it as accurate as possible. Good practice would be to complete reviews on an annual basis or sooner, if required. For example, a more frequent review may be required for higher-risk RCS exposures.
Occupational health and safety (OSH) professionals
Organisations working in the many sectors where silica can be found will need the help of their OSH professional. You will need to work with both managers and workers to help risk assess, implement controls, and eliminate or reduce RCS exposures.
You may need to:
- support with the organisational silica risk assessment
- support with identifying and implementing suitable controls by following the ‘hierarchy of control’. For example, introducing reduction, engineering, administrative controls, or advising upon suitable PPE or RPE if adequate control cannot be achieved by other means
- support with the implementation or maintenance of the silica exposure plan
- routinely inspect known RCS tasks and areas
- consult with workers on a regular basis
- check that workers are following and understand procedures and safe systems of work
- source and provide suitable silica information and training
- investigate incidents and exposures
- support with health monitoring and surveillance requirements
- support with evaluations and act on any learning lessons to prevent future RCS incidents or exposures.
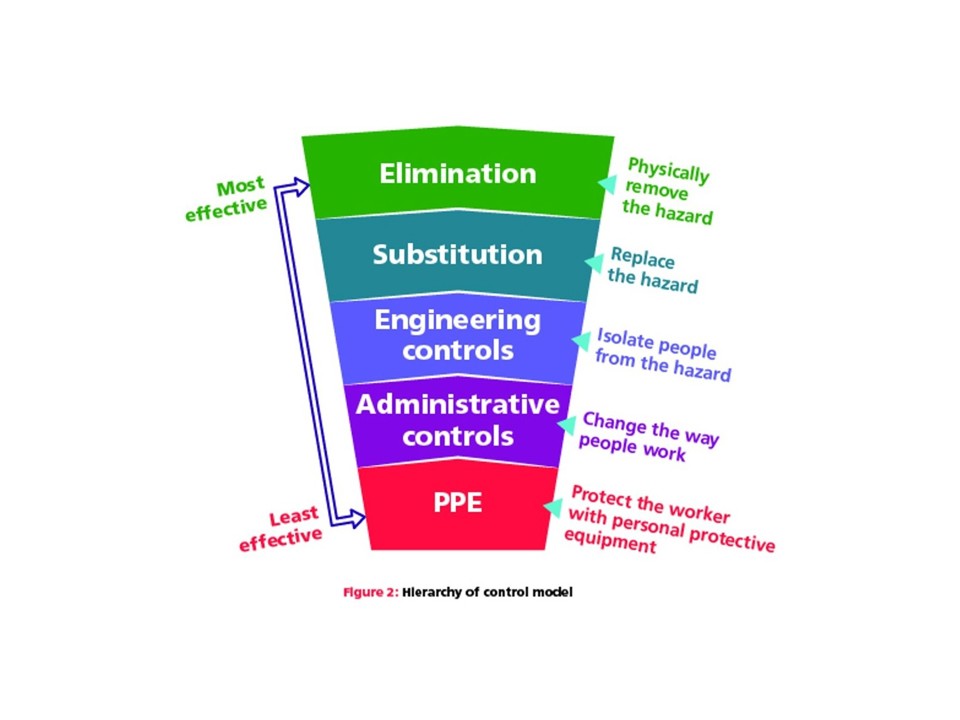
Control measures
After risk assessment, suitable controls should be identified following the hierarchy of control.
Controls should give preference to those that protect many workers at a time instead of individual worker controls.
Workers should also be consulted when implementing controls, as they will understand and have more experience of the tasks that may generate RCS dust.
- Wet-working, which involves suppressing dust and accelerating the weathering process of silica which reduces toxicity. On-tool extraction systems may also be used to capture dust particles when cutting, drilling and grinding.
- Physical barriers or computer numerical control (CNC) machines can be used to isolate areas where dust is created.
- Using H-class (HEPA-filtered) vacuum cleaners for collecting gathered dust – do not dry sweep areas. Note that dust waste bags should be sealed securely and disposed of in the appropriate waste container.
- Setting up exclusion zones to indicate boundaries to RSC dust areas.
- Signage to indicate warnings, PPE/RPE requirements and other information.
- Organising higher-exposure times to RCS for when fewer workers are on site or in an area.
- Having regular breaks and shift rotations to reduce the time workers are exposed to RCS.
- Ensuring workers are aware of the importance of washing hands thoroughly after work and before eating or drinking.
- Ensuring good housekeeping that will help to stop dust from gathering and keep work areas clean and free from clutter.
- wearers are face-fit tested and RPE fits correctly
- wearers are clean shaven to ensure a proper skin to RPE seal
- wearers are trained for use of the RPE
- the RPE is cleaned and checked before and after use
- filters and disposable RPE are changed regularly
- RPE is stored correctly
- defects are reported immediately and the RPE is not used if defected or unclean.
Eliminating RCS
Using alternative materials, for example using metallic shot, slag materials or grit instead of sand for abrasive blasting.
Reducing RCS
Reducing exposure to as low as possible by using materials with a lower silica content. For example, limestone or marble (2 per cent silica content) has significantly lower silica levels than engineered stone (90 per cent silica content).
Engineering controls
Administrative controls
PPE and RPE
Where exposure to RCS cannot be controlled by other means, appropriate PPE and RPE should be provided to all workers. This should include protective clothing such as overalls, gloves and boots. These should not be worn to travel home in, as this will increase the risk of spreading dust within workers’ vehicles, home or on to others.
In relation to RPE, procedures should be put in place to ensure that:
Exposure measuring and monitoring
RCS levels should be measured and monitored to ensure that exposure limits are not breached. Exposures should be as low as possible and below the legal exposure limit. Real-time dust exposure levels can now be obtained with new technologies.
It is important to remember that any exposure to RCS could be harmful and that exposure limits are not necessarily safe levels of exposure. They are practical guides. Therefore, any exposure should be mitigated and avoided if possible.
Workers
If you are at risk of exposure to RSC, your employer has a responsibility to manage the associated risks to your health and inform you of what you need to do. This may include:
- whether the tasks you are undertaking or the materials you are using will create dust that may contain silica
- how the task should be completed safely without exposure to or minimising your exposure to RCS
- training you need to implement any identified controls measures, eg how to use the extraction systems provided.
- providing you with PPE or RPE that it is suitable for the work and helps to reduce your exposure to RCS if it cannot be effectively done by other controls
- a face-fit test for any RPE – it is really important that you know how to wear RPE correctly
- what the process is for reporting incidents or equipment defects
- whether the organisation is monitoring your health with regular checks under a health surveillance programme.
Symptoms related to silica exposure
It is important you know the effect exposure to RCS can have on your health and how to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms that may suggest you’ve been affected. These include:
- persistent coughing
- progressive/severe shortness of breath
- difficulty in walking short distances, completing tasks, doing exercise or breathing
- unexplained fatigue and a loss of mobility
- fever
- weight loss
- chest pain.
 IOSH
IOSH